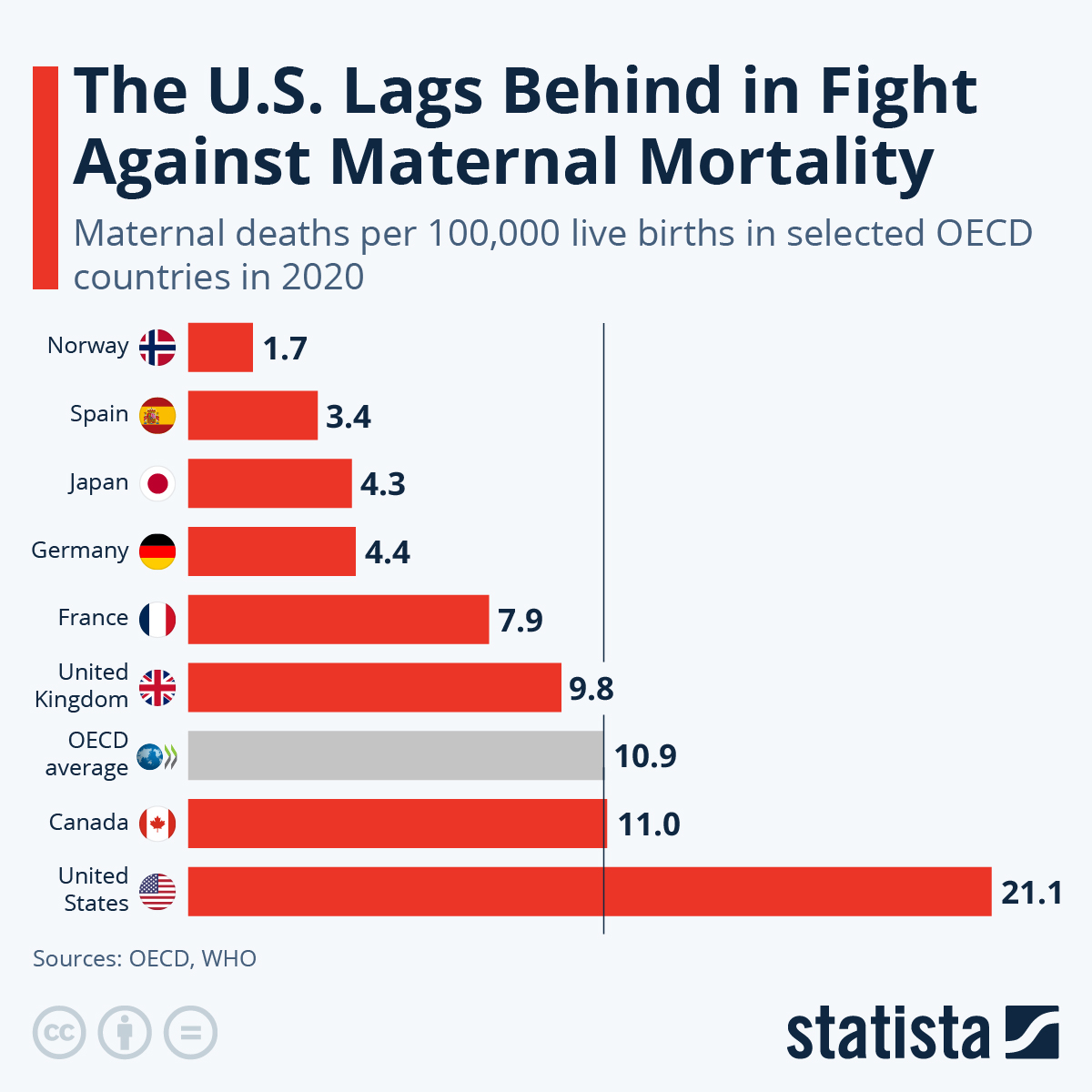
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. highlight a critical public health crisis, as more than 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. Despite this staggering statistic, the nation continues to lead high-income countries in maternal mortality, with a troubling upward trend observed between 2018 and 2022. This rise in maternal mortality reflects concerning racial disparities in maternal health; for instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Improved postpartum care and equitable access to comprehensive prenatal services are essential to combat these preventable deaths during pregnancy. Addressing systemic biases and enhancing healthcare infrastructures are urgently needed to reduce these alarming maternal mortality rates and promote better health outcomes for all mothers.
The issue of maternal deaths during childbirth and the postpartum period remains an urgent concern as the U.S. struggles to improve maternal health outcomes. High rates of maternal fatalities, particularly among marginalized racial and ethnic groups, underscore the need for reform in healthcare practices and policies. As the conversation surrounding maternal well-being grows, it is crucial to invest in robust systems that support women throughout their reproductive journeys, from pregnancy through to postpartum care. Racial inequities exacerbate the challenges faced by mothers, necessitating targeted interventions to decrease preventable fatalities. Ultimately, mobilizing healthcare resources and addressing social determinants of health will play a pivotal role in enhancing maternal health and reducing mortality rates.
Understanding the Rising Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
The issue of maternal mortality in the United States has reached alarming levels, particularly when compared to other high-income countries. With maternal mortality rates continuing to rise, it is evident that systemic changes are necessary to bring about a reduction in pregnancy-related deaths. Studies indicate that over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, emphasizing the urgent need for better healthcare policies and practices. Key contributing factors include a fragmented healthcare system, disparities in access to care, and rising prevalence of chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals.
Between 2018 and 2022, the U.S. witnessed a significant increase in maternal mortality rates, which has raised concerns among health professionals and policymakers. In 2022, the rate was reported at 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, up from 25.3 in 2018. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated these figures, particularly affecting specific demographic groups such as American Indian and Alaska Native women, who experienced a staggering mortality rate of 106.3 per 100,000 live births. These statistics underscore the need for targeted interventions to address the underlying health conditions and social determinants that contribute to these disparities.
The Role of Chronic Conditions in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Chronic medical conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, have emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths over the past several decades. The transition from hemorrhage-related deaths to those caused by cardiovascular issues has raised alarms about the health of pregnant individuals. Research indicates that many women are now entering pregnancy with underlying chronic conditions such as hypertension, which has been linked to increased mortality during and after pregnancy.
This growing prevalence of chronic conditions, especially among younger individuals, is concerning. Medical professionals have noticed a shift where pregnancy-related deaths are increasingly common in the 25 to 39 age group rather than the older demographic traditionally associated with higher risks. This shift suggests that earlier intervention and better management of chronic health issues are crucial for improving maternal health and reducing the risk of preventable deaths during pregnancy.
Addressing Racial Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
The stark racial disparities in maternal mortality rates serve as a critical indicator of the inequalities prevalent in U.S. healthcare systems. Non-Hispanic Black women, for instance, face a mortality rate of 76.9 deaths per 100,000 live births, a rate significantly higher than their white counterparts. The persistence of these disparities, despite various policy attempts to rectify them, indicates a need for a more comprehensive understanding and approach to maternal health across different racial and ethnic groups.
The findings from recent studies highlight that structural racism, access to quality care, and socioeconomic factors collectively contribute to these disparities. The healthcare system often fails to provide equitable prenatal and postpartum care, leaving marginalized groups at heightened risk of adverse outcomes. To address these inequalities effectively, stakeholders must engage in targeted policy changes that prioritize health equity and promote systemic reform aimed at creating a more inclusive healthcare landscape.
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care
Postpartum care is a critical period for maternal health that often receives insufficient attention within healthcare systems. The U.S. has traditionally defined maternal mortality as occurring within 42 days of childbirth, which overlooks the significant number of late maternal deaths that occur in the following months up to a year after delivery. The recognition of late maternal deaths—nearly a third of all pregnancy-related deaths—highlights the necessity for comprehensive care that extends well beyond the immediate postpartum period.
An extended approach to postpartum care can significantly reduce the risk of preventable maternal deaths. By ensuring that healthcare services continue well into the first year following childbirth, medical professionals can address ongoing health issues, provide support for mental well-being, and monitor chronic conditions that may have been exacerbated by pregnancy. This continuity of care is essential for ensuring better health outcomes for mothers, ultimately reducing overall maternal mortality rates.
Innovative Solutions for Improving Maternal Health
In the face of rising maternal mortality rates, the need for innovative solutions in maternal health has never been clearer. Investing in quality prenatal and postpartum care can lead to substantial improvements in health outcomes. Innovative healthcare models that prioritize accessibility, education, and comprehensive support can help address the issues that many pregnant individuals face, particularly in underserved communities.
To create lasting change, it is essential for policymakers to foster collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and families. Developing programs aimed at educating expectant mothers about their health, navigating the healthcare system, and building local support networks can empower women and lead to improved maternal outcomes. By focusing on innovation and community engagement, the healthcare system can begin to reverse the troubling trend of rising pregnancy-related deaths.
The Need for Public Health Investment in Maternal Care
Investment in public health infrastructure is crucial to addressing the rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Researchers emphasize that sustainable funding is needed to improve access to quality maternal healthcare and to develop comprehensive monitoring systems. With cuts in research funds and a deprioritization of pregnancy care, there is a risk that the necessary advances in maternal health will stagnate, further jeopardizing the lives of mothers.
Strengthening public health initiatives focused on maternal care will not only reduce preventable deaths but also ensure that maternal health remains a priority in healthcare discussions. This involves advocating for policy changes at both state and national levels, as well as securing adequate resources to support effective maternal health programs. By emphasizing maternal health in public health planning, the U.S. can work towards achieving meaningful improvements and lowering maternal mortality rates.
Healthcare Access: A Lifeline for Expecting Mothers
Access to healthcare plays a pivotal role in determining maternal health outcomes. Many women face barriers to receiving timely and appropriate prenatal care, which can lead to complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Structural issues within the healthcare system, such as lack of insurance, geographical disparities, and inadequate services in certain areas, exacerbate the challenges faced by expecting mothers.
To alleviate these issues, it is essential to develop policies aimed at improving healthcare access for all pregnant individuals. Expanding Medicaid coverage for postpartum care, providing transportation services, and fostering partnerships with community organizations can enhance access to quality care. By addressing these barriers, the U.S. can significantly lower the rates of pregnancy-related deaths and improve overall maternal health.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically affected maternal health outcomes in the U.S., exacerbating existing inequalities and increasing the risk of pregnancy-related complications. The unique challenges posed by the pandemic—such as limited access to healthcare facilities and heightened stress levels—have contributed to an alarming rise in maternal mortality rates. As healthcare systems became overwhelmed, many pregnant individuals missed critical prenatal appointments or delayed seeking care due to fears of exposure to the virus.
As we reflect on the impact of COVID-19 on maternal health, it is crucial to learn from this experience and implement changes that will safeguard maternal well-being in the future. Healthcare systems must be prepared for emergencies and ensure that maternal health services remain accessible during crises. By investing in telehealth and creating supportive resources for expecting mothers during extraordinary times, we can work towards enhancing maternal health outcomes in the long run.
Incorporating Maternal Health Education into Healthcare
Integrating maternal health education into healthcare curricula and community programs is essential for improving maternal health outcomes and reducing preventable deaths. Providing healthcare professionals with comprehensive training on the unique needs of pregnant individuals, including cultural competency and the importance of addressing racial disparities, is critical in delivering quality care. Additionally, equipping expectant mothers with knowledge about their health and available resources can empower them to make informed decisions.
Education initiatives should also focus on enhancing awareness of the warning signs of complications during and after pregnancy. By offering community workshops and informational resources, healthcare providers can help pregnant individuals recognize when to seek care, ultimately improving early intervention rates and preventing severe outcomes. By prioritizing education, the healthcare system can equip both providers and patients to navigate maternal health challenges more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current maternal mortality rates in the United States?
As of 2022, the maternal mortality rate in the United States was 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, a significant increase from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018, highlighting ongoing concerns in maternal health.
Why are pregnancy-related deaths so common in the U.S. despite being preventable?
Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are considered preventable. Factors contributing to this high maternal mortality rate include a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable access to care, and systemic bias affecting racial and ethnic groups.
How do racial disparities impact maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Racial disparities in maternal mortality rates are stark, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing a mortality rate of 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared to 27.6 for white women. This inequity is ongoing and persistent, indicating a need for targeted interventions.
What role does postpartum care play in maternal mortality rates?
Postpartum care is crucial, as nearly one third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Enhanced care during this period is needed to lower overall maternal mortality rates and address long-term health risks.
How does cardiovascular disease relate to maternal mortality rates?
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of such deaths. This shift, influenced by rising rates of chronic conditions like hypertension, emphasizes the need for improved maternal health management.
What actions can be taken to reduce maternal mortality rates?
To reduce maternal mortality rates, there needs to be a significant investment in public health infrastructure, enhanced policy initiatives to address state-level disparities, and a focus on quality care throughout the entire pregnancy and postpartum period.
Are maternal mortality rates increasing or decreasing in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have continued to rise, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. The rates observed from 2018 to 2022 reflect a concerning upward trend that demands urgent attention and action.
What is the significance of late maternal deaths in understanding maternal mortality rates?
Late maternal deaths, which occur from 42 days to one year post-pregnancy, are increasingly recognized as critical for understanding overall maternal mortality rates. These deaths underscore the importance of continuous healthcare beyond the immediate postpartum period.
How does the pregnancy-related mortality rate in the U.S. compare to other high-income countries?
The United States has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, a troubling statistic that points to systemic issues within its healthcare framework, requiring comprehensive reform to improve maternal health outcomes.
What systemic changes are needed to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
Improving maternal health outcomes requires systemic changes such as increasing access to comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care, addressing healthcare inequities, and enhancing national tracking of maternal deaths to inform better policies and practices.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates continuing to increase from 2018 to 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are considered preventable. |
| Disparities by Race and State | There are significant disparities in maternal mortality rates based on race, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates. |
| Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., surpassing hemorrhage. |
| Need for Better Healthcare Systems | There is an urgent need for improved healthcare systems and policies to address late maternal deaths and postpartum care. |
| Importance of Data Tracking | A national system for tracking maternal deaths was only fully implemented in 2018, complicating data analysis prior to that. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates are an alarming issue in the United States, where the rates continue to rise despite the fact that many of these deaths are preventable. Addressing the persistent disparities in maternal health, especially across different racial and ethnic groups, is crucial to reversing this trend. It is essential to enhance prenatal and postpartum care systems, ensuring comprehensive support for mothers beyond the immediate postpartum period. With cardiovascular disease now a leading cause of maternal death, addressing chronic health conditions and healthcare access is imperative. Focused investments in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions are necessary to improve maternal health outcomes and reduce maternal mortality rates in the U.S.