Liver cancer treatment is an area of intense research, especially considering the alarming rates of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent studies have uncovered a significant connection between bile imbalance and the progression of liver diseases, highlighting the importance of bile acids in maintaining liver health. Notably, the key molecular switch regulating bile acid metabolism, known as FXR, has emerged as a critical factor in the pathogenesis of liver cancer. Additionally, activation of YAP, a protein associated with tumor growth, disrupts normal bile acid functions, leading to further liver damage and inflammation. These groundbreaking findings pave the way for innovative treatment strategies aimed at enhancing FXR function or correcting bile acid imbalances to combat liver cancer effectively.
When discussing treatments for liver malignancies, understanding the underlying biological mechanisms is crucial. The therapeutic landscape for liver oncology is evolving, particularly with the focus on conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and their links to bile acids and liver metabolism. Recent findings suggest that disruptions in bile acid regulation, often tied to genetic and metabolic factors, can exacerbate liver diseases. Moreover, the roles of proteins like YAP in promoting tumorigenesis highlight the complexity of liver cancer pathophysiology and treatment. By exploring these intricate relationships, researchers aim to develop more effective interventions for individuals facing liver disorders.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance has become increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. This imbalance refers to the disruption in the normal production and regulation of bile acids, which are vital for both digestion and metabolic processes in the body. When the liver’s bile acid homeostasis is compromised, it can lead to liver injury, inflammation, and the progressive development of cancer. Recent studies have illuminated the pathophysiological mechanisms by which bile acid imbalances contribute to the onset of HCC.
Researchers are now focusing on critical molecular mechanisms that mediate bile production, including the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. This pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health and regulating growth, particularly in liver cells. When YAP is aberrantly activated, it can inhibit crucial bile acid receptors such as FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), compromising the liver’s ability to manage bile acids effectively. This leads to an accumulation of toxic bile acids, exacerbating liver damage and promoting tumor formation within the hepatic tissue.
The Role of YAP in Liver Cancer Progression
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has emerged as a key player in liver cancer progression, especially in its relationship with bile acid metabolism. YAP, typically known for its role in promoting cell growth and proliferation, exhibits a paradoxical function in the context of bile acid regulation. Instead of facilitating growth, activated YAP can suppress FXR, a vital sensor that maintains bile acid equilibrium. This dysregulation results in excessive bile acid production, which triggers liver inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually, hepatocellular carcinoma.
Ongoing research highlights the need to explore therapeutic strategies targeting YAP and FXR interactions to restore normal bile acid regulation. By inhibiting the repressive activity of YAP or enhancing FXR function, researchers aim to mitigate liver damage and disrupt the cancer-promoting cycle associated with bile acid imbalance. These interventions could pave the way for innovative liver cancer treatments that address not only the symptoms but also the underlying metabolic disruptions.
Exploring FXR and Bile Acid Metabolism
FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) plays a pivotal role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis and regulating liver health. This nuclear receptor coordinates bile acid synthesis and transport, ensuring that excessive bile does not accumulate in the liver, where it can cause toxicity and inflammation. The relationship between FXR and bile acid metabolism is critical for preventing liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent findings suggest that enhancing FXR signaling can promote bile acid excretion, thereby decreasing the risk of liver injury and tumor development.
The therapeutic potential of FXR agonists has garnered significant interest among researchers aiming to develop effective interventions for liver disease. By stimulating FXR activity, it may be possible to restore balance to bile acid levels and mitigate the adverse effects associated with their overproduction. Such pharmacological approaches could significantly impact the treatment landscape for liver cancer, offering new avenues to combat the disease at its metabolic roots.
Bile Acids: Implications for Liver Disease Treatment
The implications of bile acid imbalance extend far beyond mere digestion; they have significant repercussions for liver health and disease. The research surrounding the dysregulation of bile acids in liver conditions has unveiled potential therapeutic pathways. Identifying and treating bile acid imbalances could lead to innovative strategies for managing hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver-related disorders. This emerging understanding emphasizes the importance of personalized medicine approaches tailored to address bile acid dysregulation in affected patients.
Effective treatments could focus on normalizing bile acid levels and enhancing liver function through various means, such as pharmacological stimulation of FXR or promoting bile acid export. Such methods not only target the immediate biochemical imbalances but also aim to prevent the long-term complications associated with chronic liver diseases. By addressing bile imbalance, healthcare providers may improve patient outcomes and reduce the incidence of liver cancer.
Innovative Liver Cancer Treatment Strategies
As the understanding of the relationship between bile acids and liver cancer deepens, new treatment strategies are emerging that may revolutionize how we approach liver disease. The identification of pathways such as YAP and FXR opens up a wealth of potential interventions that could disrupt the cycle of liver inflammation and tumor growth. Researchers are actively pursuing the development of drugs that either activate FXR or inhibit YAP’s detrimental effects, seeking to restore a more favorable environment for liver cell health and function.
These innovative approaches not only provide hope for more effective liver cancer treatments but also aim to personalize therapy based on the unique metabolic profiles of individual patients. Tailoring treatment to the specific mechanisms of bile acid imbalance could significantly enhance the effectiveness of existing therapies and improve the chances of favorable outcomes in liver cancer patients.
The Basis of Bile Acid Sensing in Cancer
Bile acid sensing is increasingly recognized as a crucial aspect of liver physiology and pathology, particularly in the context of cancer development. The FXR receptor plays a fundamental role in detecting bile acids and orchestrating responses that protect the liver from damage. When bile acid levels become imbalanced, it can lead to a breakdown of normal liver function, opening the door to liver injuries and cancerous transformations. Thus, understanding how bile acids influence cancer biology is critical for developing effective treatments.
Research indicates that the crosstalk between bile acid signaling and cancer mechanisms is complex and multifaceted. By unraveling this complexity, scientists hope to identify biomarkers that could predict an individual’s risk for liver disease. Additionally, these insights into bile acid sensing could lead to novel therapeutic targets, enhancing our ability to combat hepatocellular carcinoma and improve liver health overall.
Potential Pharmacological Applications of FXR in Liver Cancer
The potential pharmacological applications of FXR agonists in treating liver disease and cancer are generating considerable excitement in the medical community. Activating FXR can help restore bile acid homeostasis, combat inflammation, and potentially reverse fibrosis, all of which are critical in preventing the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Given the promising preclinical data, a number of clinical trials are underway to assess the efficacy of FXR-targeting therapies in liver cancer.
Moreover, these therapeutic strategies are particularly appealing as they offer a dual benefit: addressing both the symptoms of chronic liver disease and the underlying mechanisms that contribute to tumor formation. By focusing on FXR modulation, researchers are optimistic that they can improve patient prognosis and offer new hope for individuals diagnosed with liver cancer.
Emerging Research on Bile Acid Metabolism
Emerging research on bile acid metabolism is shedding light on the intricate connections between metabolic dysfunction and liver cancer. Understanding how bile acids interact with various signaling pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway, provides valuable insights into the mechanisms driving hepatocellular carcinoma. This growing body of work emphasizes the importance of investigating the role of bile acids beyond their traditional functions, as they increasingly emerge as critical players in liver pathology.
Advanced research techniques are being employed to dissect the complex interactions between bile acids and liver cancer. Such studies are vital for uncovering novel biomarkers that could serve as early indicators of disease progression or response to treatment. As research continues to evolve, the hope is that it will lead to innovative strategies that harness the therapeutic potential of bile acid modulation in liver cancer management.
Conclusion: The Future of Liver Cancer Treatments
As research continues to advance our understanding of liver biology and the role of bile acids in liver disease, the future of liver cancer treatments appears promising. The insights gained from recent studies regarding the YAP and FXR pathways could lead to breakthrough therapies aimed at restoring bile acid balance and preventing cancer progression. Continued exploration of the molecular mechanisms behind bile acid imbalance will be crucial in developing targeted interventions.
Moreover, integrating findings on bile acid signaling into clinical practice could transform how liver diseases are diagnosed and treated. By adopting a more nuanced approach to managing liver health and cancer, healthcare professionals may enhance therapeutic outcomes for patients. The journey towards effective liver cancer treatments is ongoing, but with each discovery, we move closer to developing more effective strategies that could save lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
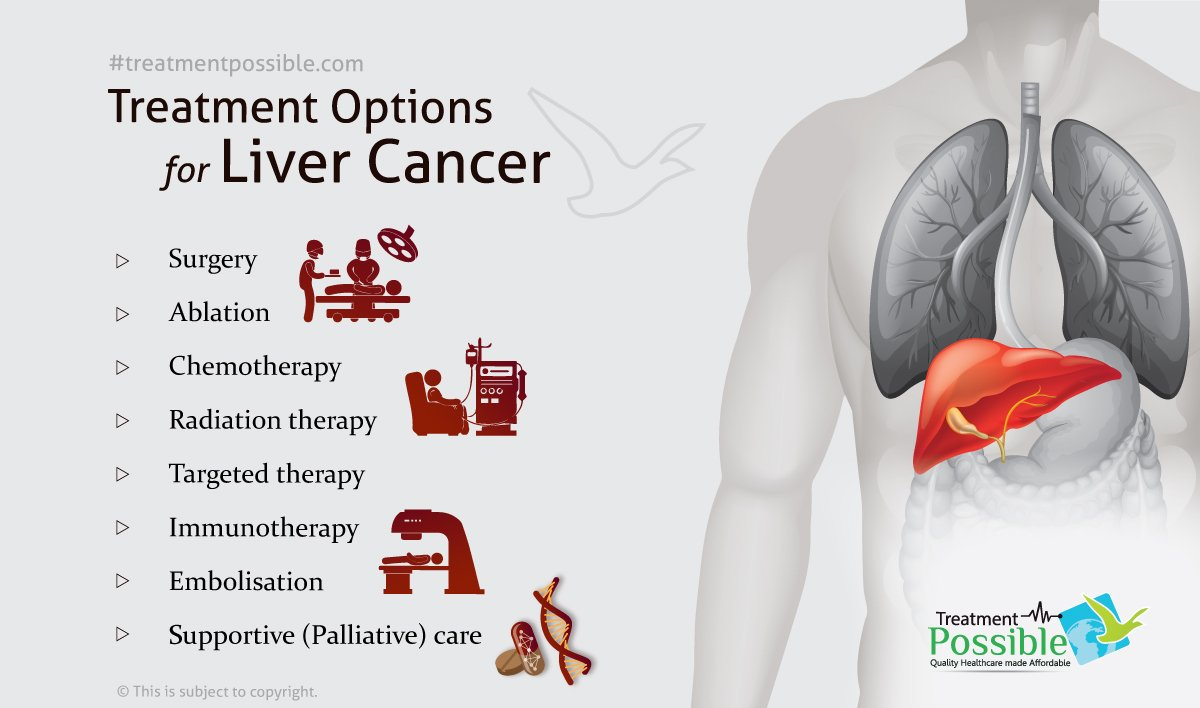
What are the current liver cancer treatment options?
Current liver cancer treatment options include surgical resection, liver transplantation, ablation therapies, embolization, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy. Each option varies depending on the cancer stage, patient health, and liver function.
How does bile acid metabolism impact liver cancer treatment?
Bile acid metabolism significantly impacts liver cancer treatment as an imbalance in bile acids has been linked to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therapies targeting this imbalance, such as enhancing FXR function, may improve treatment outcomes.
What role does YAP play in liver cancer treatment strategies?
YAP, a key regulator in cell growth and metabolic processes, plays a critical role in liver cancer treatment strategies. Blocking YAP’s repressive action can enhance bile acid metabolism and reduce liver damage, making it a target for potential treatments.
Can FXR activation help in liver cancer treatment?
Yes, activating FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) can help in liver cancer treatment by promoting bile acid homeostasis and reducing inflammation and fibrosis. This mechanism may slow the progression of liver cancer and improve patient outcomes.
What is the importance of bile imbalance in liver disease and cancer?
Bile imbalance is crucial in liver disease and cancer as it can lead to inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately resulting in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding and treating this imbalance can open new avenues for effective liver cancer therapies.
Are there experimental treatments targeting bile acids for liver cancer?
Yes, experimental treatments targeting bile acids for liver cancer include pharmacological agents that stimulate FXR or enhance bile acid excretion. These strategies aim to correct bile acid imbalances and inhibit liver cancer progression.
How can lifestyle changes affect liver cancer treatment outcomes?
Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding alcohol, can positively affect liver cancer treatment outcomes by improving liver function and overall health, thus supporting conventional therapies.
What are the research directions for liver cancer treatment targeting bile acids?
Research directions for liver cancer treatment targeting bile acids include investigating YAP and FXR interactions, exploring pharmacological agents to restore bile acid homeostasis, and developing therapies to promote bile acid excretion.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Bile acids produced by the liver are crucial for digesting fats but their imbalance can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Molecular Switch | A key molecular switch has been identified that regulates bile acid metabolism, providing insights for liver cancer treatment. |
| Role of YAP | YAP acts as a repressor in bile acid metabolism, hindering the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), leading to liver damage and cancer. |
| Potential Interventions | Strategies include stimulating FXR function, inhibiting HDAC1, or promoting bile acid excretion to reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Implications | The findings reveal broader implications for understanding nutrient sensing and metabolic control in liver biology and cancer. |
Summary
Liver cancer treatment has been significantly advanced by recent research highlighting the critical role of bile acids and molecular signaling pathways. A key discovery has revealed that an imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers, led by Yingzi Yang, have identified the YAP protein’s unexpected role in regulating bile acid metabolism, suggesting new therapeutic avenues. By targeting the YAP protein and enhancing the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), potential treatments could emerge to combat liver cancer effectively. These findings not only open doors for pharmacological approaches but also deepen our understanding of liver biology and its role in cancer progression.